English lessons for kids in Midland, Georgia

For nearly 30 years, RTL English has been taught in schools, tutorial centres & at home both as part of the curriculum and as a supplementary activity. RTL English is growing in popularity worldwide, so why not join hundred of thousands of parents, tutors & teachers around the globe and teach your son or daughter RTL English today?
Teaching your son or daughter to use English confidently might very well be the key to his or her success in school in Georgia, in exams, in his or her career and beyond.
Teaching English to your son or daughter might be the key, not only to his or her success in school in Midland, but also their sense of self-worth, both in Georgia and beyond.
Elaine Shannon, Author & Curriculum Designer Tweet
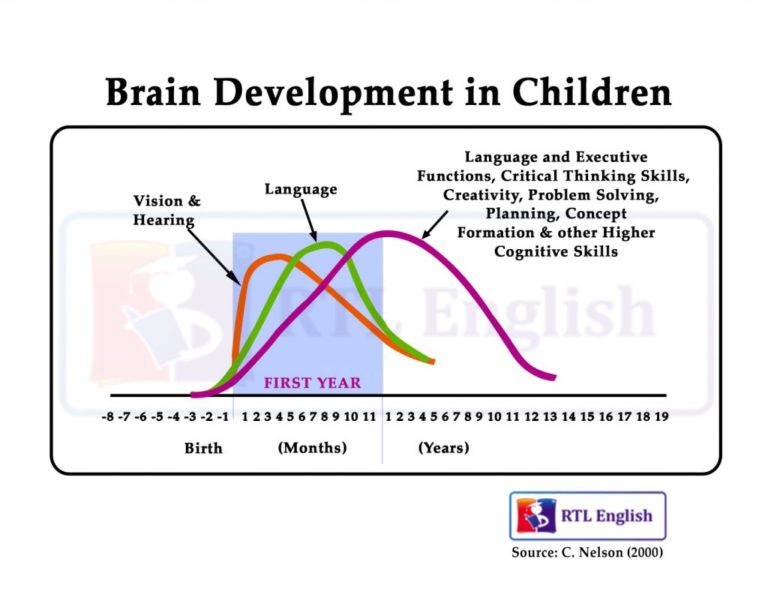
- Early & advanced English skills will make your child smarter.
- Early & advanced English skills will improve problem solving.
- Early & advanced English skills will improve planning, & abstract thinking skills.
- Early & advanced English skills will help develop complex idea comprehension.
- Early reading can help children compensate for modest levels of ability in other areas. (*Ref)
ON A PRACTICAL LEVEL, HOW IMPORTANT IS EARLY READING?
- Your child’s reading ability and vocabulary at 3 years old might predict his or her success in school in Midland when they are 6 to 7 years old (*Ref).
- Your child’s reading ability at 6 to 7 years old might predict their success at 17 to 18 years old (*Ref)!
- Your child’s reading ability at 7 to 8 years old might determine their graduation from senior school in Midland (*Ref).
ON THE OTHER HAND:
- Children who can’t read competently by 7 to 8 years old are four times more likely to leave school without a diploma/results than proficient readers (*Ref).
and:
- Children who are not taught Phonemic Awareness, & therefore have to rely on memory have difficulty beginning to read and continue to have difficulty with new words.
BUT, SURELY SCHOOL WILL TEACH MY CHILD TO READ? SO, WHY DO I NEED TO BOTHER?
If this is what you are thinking, then you should know that you cannot rely on schools, including those in Midland …
- In the USA, almost 70% of children at school who are aged 9-10 years old cannot read proficiently (*Ref)!
- And, of those children, 33% of them read at only a very basic level, and 34% are reading at a very unsatisfactory level (*Ref).
- It’s not much different in the UK, where over 100,000 children leave school illiterate(*Ref).
- Or in Australia, where 33% of students aged 11 years old fail to meet literacy benchmarks (*Ref).
- Or in Canada, where 42% of the entire adult population is only semi-illiterate (*Ref).
NO, YOU CANNOT RELY ON SCHOOLS.
But, why not?
- Teachers don’t always understand the basic building blocks of language & reading
- Teachers often don’t know how to teach English language concepts
- There just aren’t enough qualified teachers
- Classes are too over-crowded
- Kids don’t get enough attention from teachers in the classroom
- Schools aren’t using the correct teaching systems – i.e they rely on rote learning or sight words
- Schools are overwhelmed and have tried to shift some of the burden of teaching onto apps & computers
UNFORTUNATELY, IT IS A FACT THAT:
Being illiterate is a guaranteed ticket to a dead end.
YOU NEED TO TAKE CHARGE OF YOUR CHILD’S EDUCATION – TODAY!
BUT HOW?
You can begin by teaching English to your child.
By Teaching your child to read your son or daughter will develop early reading skills that will help put them years ahead of other children in Georgia. So, if you’ve decided that you want to become a proud parent of a happy and smart son or daughter, then you owe it to your son or daughter to teach them to read and improve their English.
WE HELP PARENTS TEACH ENGLISH TO CHILDREN
RTL English™ offers 600 easy-to-teach & downloadable English lessons for parents to teach to their child at home. Our workbook lessons will help your child to catch up, keep up & get ahead! Our lesson workbooks also challenge more advanced students; so whatever your son or daughter’s ability, there’s sure to be an RTL English lesson that’s suitable for them.
THE RTL ENGLISH CURRICULUM CONSISTS OF 15 YEARS (LEVELS) OF TEACHING MATERIALS WHICH INCLUDE SIX HUNDRED WORKBOOKS COMPRISING FOUR THOUSAND WORKSHEETS & NINETEEN THOUSAND TEACHING INSTRUCTIONS & WILL SAVE YOU OVER 2,000 DAYS OF LESSON PREPARATION TIME!
Foundation Stage
Includes Level 1, 2 & 3.
Suitable for kids aged 3-6 years old in Midland, Georgia
Elementary Stage
Includes Level 4, 5 & 6.
Suitable for kids aged 6-9 years old in Midland, Georgia
Intermediate Stage
Includes Level 7, 8 & 9.
Suitable for kids aged 9-12 years old in Midland, Georgia
Upper Intermediate Stage
Includes Level 10, 11 & 12.
Suitable for kids aged 12-15 years old in Midland, Georgia
Advanced Stage
Incl. Level 10, 11 & 12.
Suitable for kids aged 15-18 years old in Midland, Georgia
Winning Awards Since 1996
With 24 years of research, development, dedication and experience, RTL English is committed to offering the best possible start to English language learners worldwide. RTL English is part of the Ready To Learn group, an international educational organisation with students worldwide.
Elaine Shannon founded Ready To Learn in 1996, and is an internationally respected author, language expert and School Principal with more than 40 years of specialist experience. Elaine & her team of instructional designers, linguists and educational experts developed the RTL English Curriculum.
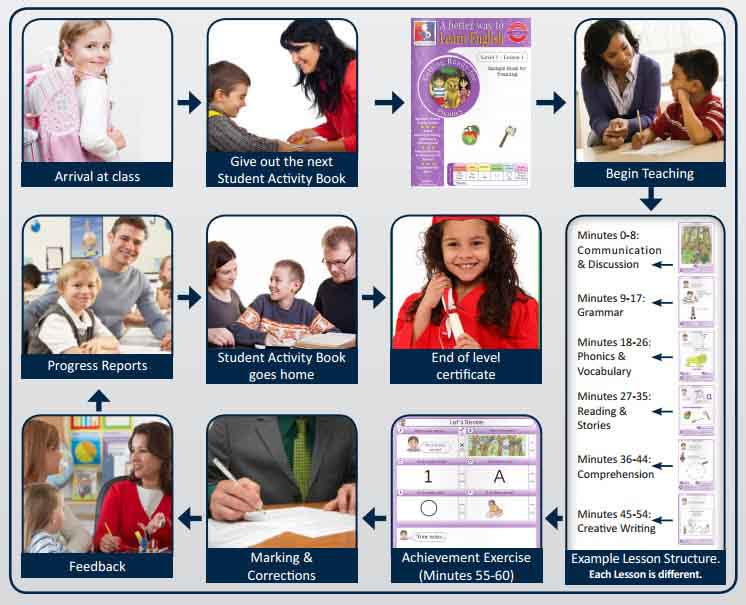
What Happens In A Lesson?
- Each lesson is designed to last approximately 60 minutes. Normally, your child will spend 55 minutes participating in learning activities, and 5 minutes completing an achievement exercise that’s used to reinforce the lessons’ learning designs & objectives.
- Each lesson is accompanied by an RTL English lesson workbook. The workbook consists of six worksheets of instructional content and one reinforcement exercise page.
- You will use the workbook & teaching notes to guide and lead your child through the variety of learning activities in the workbook.
- Although all of our workbooks follow a similar format, each one is slightly more challenging than the last in the sequence. As a result, your child will be able to advance in small manageable steps & acquire English language skills that will last them a lifetime.
- There are 5 learning stages, 15 learning levels and 600 lessons in the RTL English curriculum.
- Your child will need to complete 36 lessons to finish one learning level – which lasts approximately 1 academic year.

What Will My Child Be Taught?
It depends on your child’s age and their English language ability. To find out what your child will be taught, please click the grey button & then click the book cover that’s closest to your child’s current age → Lesson Workbooks
The RTL English Curriculum teaches all the communicative functions and language forms your child will need to succeed in school, exams and beyond, including:
- Phonemic Awareness
- Alphabetic Principle
- Systematic & Explicit Phonics
- Fluency with Text
- Proficient Grammar Knowledge
- Creative Writing
- Expanded Vocabulary
- Advanced Comprehension, and
- Confident Speaking Skills
The RTL English Curriculum: Kids 3 to 18 Years Old
Whatever your son or daughter’s age or English language ability, there is sure to be an RTL English course (aka ‘level’) that will help your son or daughter learn or improve his or her English. This is because our curriculum provides 15 years of learning for child aged 3 to 18 years old and teaches all the communicative functions & language forms your son or daughter will need to have a richer, more successful educational experience. RTL English will also supplement your child’s learning at their school in Midland.
The RTL English Curriculum consists of 15 years (levels) of teaching materials which include 600 workbooks (comprising 4,000 worksheets & 19,000 teaching notes) & saves over 2,000 days of preparation time.Level 1
Kids: 3-4 years old
36 lessons. 36 workbooks. 252 worksheets. 1134 teaching instructions.
Level 2
Kids: 4-5 years old
36 lessons. 36 workbooks. 252 worksheets. 1134 teaching instructions.
Level 3
Kids: 5-6 years old
36 lessons. 36 workbooks. 252 worksheets. 1134 teaching instructions.
Level 4
Kids: 6-7 years old
36 lessons. 36 workbooks. 252 worksheets. 1134 teaching instructions.
Level 5
Kids: 7-8 years old
36 lessons. 36 workbooks. 252 worksheets. 1134 teaching instructions.
Level 6
Kids: 8 -9 years old
36 lessons. 36 workbooks. 252 worksheets. 1134 teaching instructions.
Level 7
Kids: 9-10 years old
36 lessons. 36 workbooks. 252 worksheets. 1134 teaching instructions.
Level 8
Kids: 10-11 years old
36 lessons. 36 workbooks. 252 worksheets. 1134 teaching instructions.
Level 9
Kids: 11-12 years old
36 lessons. 36 workbooks. 252 worksheets. 1134 teaching instructions.
Level 10
Teens: 12-13 years old
36 lessons. 36 workbooks. 252 worksheets. 1134 teaching instructions.
Level 11
Teens: 13-14 years old
36 lessons. 36 workbooks. 252 worksheets. 1134 teaching instructions.
Level 12
Teens: 14-15 years old
36 lessons. 36 workbooks. 252 worksheets. 1134 teaching instructions.
Level 13
Teens: 15-16 years old
36 lessons. 36 workbooks. 252 worksheets. 1134 teaching instructions.
Level 14
Teens: 16-17 years old
36 lessons. 36 workbooks. 252 worksheets. 1134 teaching instructions.
Level 15
Teens: 17-18 years old
8 lessons. 8 workbooks. 56 worksheets. 252 teaching instructions.
Can I See A Lesson Workbook?
There are 600 workbooks like the one below. Lesson 19, Level 1 below suits children between 3 and 4 years old. To see an example of a lesson workbook that is likely to suit your child, please click the grey button & then click the book cover that’s closest to your child’s current age → Lesson Workbooks
What Method Do You Use?
- We teach using a Step-by-Step method. The content of each lesson is determined by an 8-page workbook that’s slightly more challenging than the last in the sequence. Lessons ‘scaffold’ and build upon the learning of the previous lesson. As a result, students advance in small, manageable steps and acquire English language skills that enable them to achieve better results in school, exams & beyond..
- Sequenced instruction is organised into 5 developmentally appropriate stages, 15 levels of increasing difficulty and 600 lessons. Each lesson provides one hour of learning per week and follows a workbook that consists of six worksheets with instructional content and one reinforcement exercise page.:
- Each lesson is accompanied by a workbook follows a similar plan:
- Page 1 :: Communication/ Discussion/ Topic orientated
- Page 2 :: Grammar/ Language
- Page 3 :: Phonics/ Vocabulary
- Page 4 :: Reading (Ongoing Story)
- Page 5 :: Story Comprehension/ Language
- Page 6 :: Grammar/ Language Exercise
- Page 7 :: Achievement Exercise / Assessment
- Depending on your child’s age and their English skills, instruction will typically consist of a variety of activities including speaking, listening, letter-sound correspondence, sight words, guided oral reading, text comprehension, creative writing, grammar and critical thinking.
- You don’t need to prepare anything or create teaching materials for an RTL English lesson. It’s all been done for you. Each page of this workbook contains teaching notes to enable you to guide and lead your child through the learning activities. Once your son or daughter has finished their lesson, record their achievements in the progress report form and then simply print the next workbook in the sequence.
Will My Child Learn Phonics?
- Yes! We teach synthetic & analytical phonics which includes 44 basic phonemes, 22 beginning blends and 15 ending blends.Our students learn and practise phonics throughout our Foundation, Elementary, Intermediate and Upper Intermediate stages. Our Advanced stage uses phonics to teach pronunciation.
- We pay particular attention to blended consonant sounds (that are located at the beginning and end of many words). We teach vowels first and then consonants. As soon as possible we teach children to read. In practice this means after students have learnt 5 vowel sounds and 2 consonants they can read a few words by themselves. Children are also taught how to decode words, so from the very beginning they can see new simple words and know how to read them.
Coordinates: 42°00′N 43°30′E / 42.000°N 43.500°E / 42.000; 43.500
Georgia (Georgian: საქართველო, romanized: sakartvelo; IPA: [sɑkʰɑrtʰvɛlɔ] (![]() listen)) is a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the south by Turkey and Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital and largest city is Tbilisi. Georgia covers a territory of 69,700 square kilometres (26,911 sq mi), and its approximate population is just about 3.718 million. Georgia is a unitary parliamentary republic, with the doling out elected through a representative democracy.
listen)) is a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the south by Turkey and Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital and largest city is Tbilisi. Georgia covers a territory of 69,700 square kilometres (26,911 sq mi), and its approximate population is just about 3.718 million. Georgia is a unitary parliamentary republic, with the doling out elected through a representative democracy.
During the classical era, several independent kingdoms became received in what is now Georgia, such as Colchis and Iberia. The Georgians officially adopted Christianity in the early 4th century. The Georgian Orthodox Church had huge importance for the spiritual and diplomatic unification of beforehand Georgian states. The unified Kingdom of Georgia reached its Golden Age during the reign of King David the Builder and Queen Tamar the Great in the 12th and to the front 13th centuries. Thereafter, the kingdom declined and eventually disintegrated below the hegemony of various regional powers, including the Mongols, the Ottoman Empire and successive dynasties of Iran. In the late 18th century, the eastern Georgian Kingdom of Kartli-Kakheti forged an alliance similar to the Russian Empire, which directly annexed the kingdom in 1801 and conquered the western Kingdom of Imereti in 1810. Russian rule greater than Georgia was eventually traditional in various friendship treaties in imitation of Iran and the Ottomans and the unshakable Georgian territories were absorbed by the Russian Empire in a piecemeal fashion through the course of the 19th century.
During the Civil War taking into account the Russian Revolution in 1917, Georgia briefly became portion of the Transcaucasian Federation and later emerged as an independent republic since the Russian army violent behavior in 1921, which normal a presidency of workers' and peasants' soviets. Soviet Georgia was incorporated into a further Transcaucasian Federation and became a founding republic of the Soviet Union in 1922. In 1936, the Transcaucasian Federation was dissolved and Georgia emerged as a Union Republic. During World War II, almost 700,000 Georgians fought in the Red Army adjoining the Germans. After Soviet leader Joseph Stalin, a native Georgian, died in 1953, a appreciation of ruckus spread next to Nikita Khrushchev and his de-Stalinization reforms, leading to the death of approximately one hundred students in 1956.
By the 1980s, an independence hobby was acknowledged and grew, leading to Georgia's secession from the Soviet Union in April 1991. For most of the in the same way as decade, post-Soviet Georgia suffered from civil conflicts, secessionist wars in Abkhazia and South Ossetia, and economic crisis. Following the bloodless Rose Revolution in 2003, Georgia strongly pursued a pro-Western foreign policy; aimed at NATO and European integration, it introduced a series of democratic and economic reforms. This brought about impure results, but strengthened permit institutions. The country's Western orientation soon led to the worsening of relations when Russia, culminating in the brief Russo-Georgian War in August 2008 and Georgia's current territorial dispute in the same way as Russia.
Georgia is a developing country and ranks 70th upon the Human Development Index. The country is a zealot of the United Nations, the Council of Europe, and the GUAM Organization for Democracy and Economic Development. It contains two de facto independent regions, Abkhazia and South Ossetia, which gained extremely limited international confession after the 2008 Russo-Georgian War. Most of the world's countries announce the regions to be Georgian territory under Russian occupation.
Academic References
- The Cognitive Foundations of Learning to Read: A FrameWork Sebastian Wren
- The relatonship of phonemic awareness to reading acquisiton: more consequence than preconditon but still important. Wimmer H, Landerl K, Linortner R, Hummer P. University of Salzburg, Austria.
- NAEP 1998 Reading Report Card for the Nation and the States March 1999 Authors: Patricia L. Donahue, Kris n E. Voelkl, Jay R. Campbell, and John Mazzeo
- National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. (2000). Report of the National Reading Panel. Teaching children to read: An evidence-based assessment of the scientific research literature on reading and its implications for reading instruction (NIH Publica on No. 00-4769). Washington, DC: U.S. Government Prin ng Office.
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Functional_illiteracy
- J Learn Disabil. 2009 Sep-Oct;42(5):392-402. Epub 2009 Jun 19. Why elementary teachers might be inadequately prepared to teach reading. Joshi RM, Binks E, Hougen M, Dahlgren ME, Ocker-Dean E, Smith DL.
- Australia Government Department of Educa on, Science and Training: htt p://www.dest.gov.au/archive/schools/literacy&numeracy/charts.html
- CBC News: Canada’s Shame – h p://www.cbc.ca/news/background/educa on/canada-shame.html
- The Timing and Quality of Early Experiences Combine to Shape Brain Architecture Center on the Developing Child, Harvard University
- Vocabulary Development and Instruc on: A Prerequisite for School Learning Andrew Biemiller, University of Toronto iii. Early reading acquisiton and its relation to reading experience and ability 10 years later. Cunningham AE, Stanovich KE.
- Double Jeopardy How Third-Grade Reading Skills and Poverty Influence High School Gradua on Donald J. Hernandez, Hunter College and the Graduate Center
- What Reading Does for the Mind ANNE E. CUNNINGHAM and KEITH E. STANOVICH